Introduction
AMD10 is a cosmic rays detector, it works with 4 Geiger-Müller tubes, type Si22G (160 x Ø18 mm usefull surface).
This detector was ideated to get an high rate of measurement in comparison to detectors with one single channel, moreover the three channels have different geometry thus they "see" incoming cosmic rays from different directions.
Description
As for every cosmic ray detector, is considered as single cosmic ray (muon) only a particle that cross at least two counters aligned along an axis, this because muons are very energetic particles and can travel through many meters of material (hundreds) without lose energy in a perceptible way.
From the schematic below, you can see that every single channel is formed from a couple of GMT (1-4, 2-4, 3-4). The second channel, the central one, (GMT 2-4) points to the Zenith, instead the right and left channels are inclined by 10°, nevertheless the geometry lets every channel to frame a (plain) angle equal to 10°, so the instrument as a whole has 30° of field of view.
Aims:
AMD10 at first was conceived with the aim to do measurements about cosmic ray absorption in materials and intensity loss in rocks or to hazard measurement about muon tomography - always in educational purview - furthermore, contemporary measurement on three channels permits a quick clue on many aspects: the dependence from the zenital angle, the latitude effect and the the east-west effect; this detector will also be employed as support on the ADA project, a network of cosmic ray detectors in Italy and Switzerland.
Technics:
The detector has several settings, according on the measurement type, you can select a channel one by one or get the data from all the channels, thus the total muons crossing the detector. Having three channels complicate a bit the data acquisition procedure, so a new version of the AstroRad software is incoming to get data from all the channels at the same time. AMD10 however has several outputs to connect other devices such as microprocessors, data-logger and so on.

AMD10 connected to a tablet pc
AMD10 videoclip
First data
Results from a very first test, with a "standard" setting give us a mean rate of 27 cpm (muons per minute) considering all the channels together, a good rate for our expected aims.
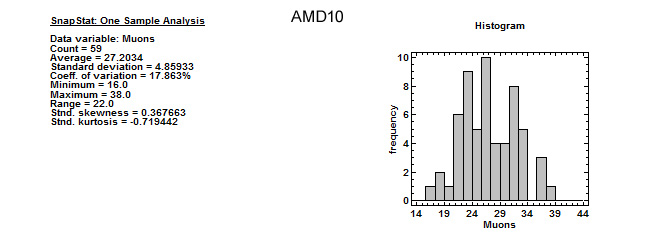
Statistics of the first test
In the next months will follow practical applications with the use of this new cosmic ray detector.
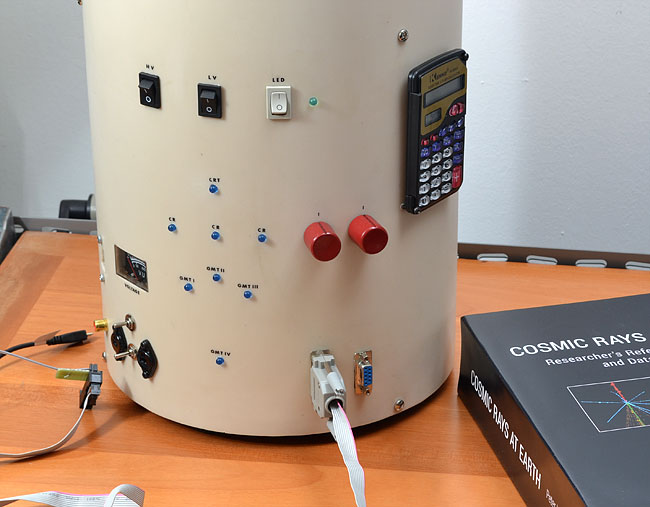

AMD10 -in the foreground connections to computers and other peripherals
Some phases of the construction

I Raggi Cosmici possono spiegare la formazione dei pianeti rocciosi 16.01.2025
Una questione chiave in astronomia è quanto siano onnipresenti i pianeti rocciosi simili alla Terra. La formazione di pianeti terrestri nel nostro Sistema Solare è probabilmente stata fortemente influenzata dal calore di decadimento radioattivo di radionuclidi a vita breve (SLR), in particolare 26Al (alluminio-26), probabilmente emessi da supernovae vicine. Tuttavia, i modelli attuali faticano a riprodurre l'abbondanza di SLR desunta dall'analisi dei meteoriti senza distruggere il disco protosolare. Un nuovo studio propone il meccanismo di "immersione", in cui la nucleosintesi dei raggi cosmici in un'onda d'urto di supernova riproduce le abbondanze stimate di SLR a una distanza di supernova superiore a quella prevista dal meccanismo di "iniezione" classico da supernove vicine. A supporto di questo scenario, si stima che le stelle di massa solare negli ammassi stellari sperimentino tipicamente almeno una di queste supernovae entro 1 parsec. Ciò suggerisce che le abbondanze di SLR simili a quelle del Sistema Solare e la formazione di pianeti terrestri siano più comuni di quanto si pensasse in precedenza...

Fonte: Science Advances
Il libro AstroParticelle
26.09.2013 - Un viaggio scientifico tra i raggi cosmici raccontato attraverso la storia, le invenzioni i rivelatori e gli osservatori; senza trascurare gli effetti che essi producono coinvolgendo numerose discipline scientifiche tra cui astrofisica, geofisica e paleontologia.
Accedi | Registrati